Since AWS Cognito is an IDP that provides password-based authentication only, AWS Cognito has partnered with Mosaic to seamlessly integrate into their authentication experience to passwordless authentication based on WebAuthn, which is based on FIDO2 biometrics. This solution requires end-users to register a single account with your business and then log in with a fingerprint or facial biometric on any channel and any device.
This article illustrates how to integrate Mosaic's passwordless authentication into applications relying on AWS Cognito as their IDP. With passwordless authentication enabled, users who will request to authenticate from your app will be presented with both AWS login methods and WebAuthn and will freely choose the method they prefer.
Here's a preview of the passwordless authentication/registration flow enabled by the integration. More details below.
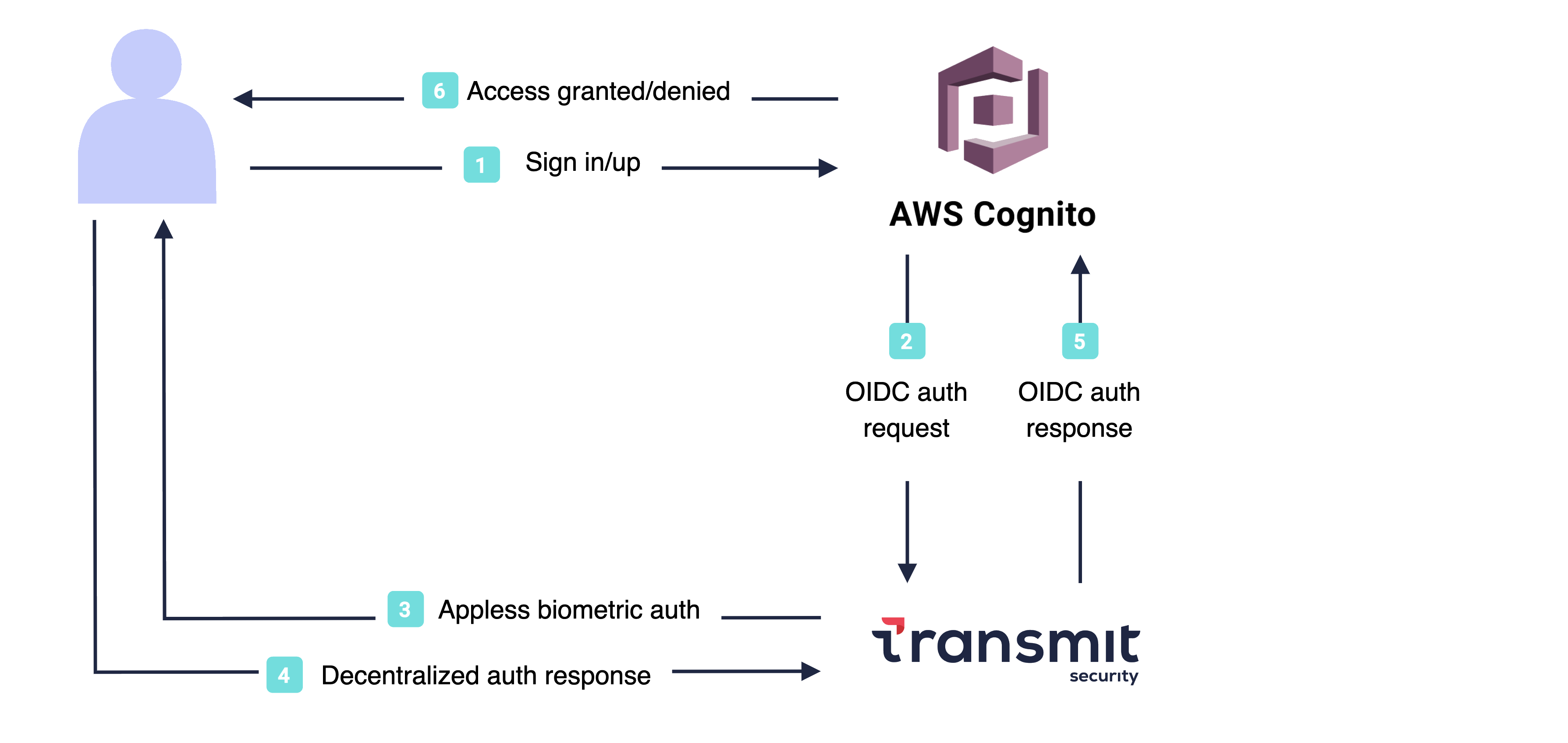
The integration between Mosaic hosted login and AWS Cognito depends on account linking, specifically, the synchronization of user-identifying data. To ensure account linking, users must be identified by either email or phone number in both apps. On the Mosaic side, both identifiers undergo OTP verification before registering credentials.
When a user requests to log in with biometrics, Mosaic's hosted experience will manage all the logic to proceed either with a WebAuthn registration or authentication. As a result, if a user attempts to log in without an existing profile, the flow will create a new user in Mosaic.
Here's a sample flow that illustrates the logic behind Webauthn registration:
- In AWS Cognito login XP, the user requests to log in with biometrics.
- AWS Cognito redirects the browser to Mosaic's hosted XP.
- Transmit:
- Collects a user identifier, either an email or phone number.
- Verifies the identifier using OTP verification.
- Creates a new user if no user is found for the user identifier.
- Registers biometrics to the identified user.
- Redirects back to AWS Cognito with an authorization code.
- AWS Cognito exchanges the authorization code for an ID and access tokens.
- AWS Cognito processes the tokens, that is:
- Validates the tokens.
- Identifies the user based on email or phone.
Here's a sample flow that illustrates the logic behind Webauthn authentication:
- In AWS Cognito login XP, the user requests to log in with biometrics.
- AWS Cognito redirects the browser to Mosaic's hosted XP.
- Transmit:
- Authenticates the user using the WebAuthn credentials registered on the device.
- Redirects back to AWS Cognito with an authorization code.
- AWS Cognito exchanges the auth code for ID and access tokens.
- AWS Cognito processes the tokens, that is:
- Validates the tokens.
- Identifies the user based on email or phone.
Before you delve into the procedure ensure you have access to an AWS Cognito app that identifies users through email or phone number. Identifying users through these methods is crucial to allow account linking between AWS and Mosaic.
Add the AWS Cognito redirect endpoint as an allowed redirect URI in your Mosaic app. After Mosaic authenticates the user, Mosaic will redirect back to AWS Cognito with an authentication code that will later be exchanged for an ID and access token. The redirect URI is provided by AWS Cognito and based on you app's domain in AWS Cognito.
It should respect the following format: https://YOUR_AWS Cognito_DOMAIN.auth.us-east-1.amazoncognito.com/oauth2/idpresponse
If you don't already have an application, you'll need to create one first (see Create application).
In Mosaic's Admin portal > B2C or B2B Identity based on your setup > Experience Management, configure the authentication experience:
- For the User identifier set either the email or phone number, according to the identifier also used in your AWS Cognito app.
- For the Primary authentication method set the Passkey.
- For the Secondary authentication method set:
- WebAuthn QR, to provide an alternative login option in case biometric authentication is not supported on the device (for example, if a desktop device lacks biometric scanners).
- Email OTP or SMS OTP (on the basis of the selected user identifier) to enable OTP verification of the user identifier.
- Remove all options that are activated by default in the Select user information section. The collection of user information is managed by AWS Cognito as the primary IDP.
- (Optional) Activate the Sign-in/Sign-up flow toggle to enable seamless redirection to the sign-up page for users attempting to log in with an unregistered user account. In this case, when the user clicks the login button, the system will automatically initiate OTP verification for the email or phone number in order to proceed with sign-up.
From the AWS Cognito main page, navigate to User pools, select Create user pool and then create a user pool.
In the user pool Sign-in Experience settings, set up Mosaic as an OIDC federated identity provider. Here's a summary of the information expected for this setup:
- Client ID and Client secret of your Mosaic app (available in your Mosaic app in the Admin Portal)
- Authorized scopes:
openid emailoropenid phonedepending on the identification method chosen for the integration. - Attribute request method:
GET - Setup method set on Manual input, and filled with the following values:
- Issuer URL:
https://userid.security - Authorization endpoint:
https://api.transmitsecurity.io/cis/oidc/auth - Token endpoint:
https://api.transmitsecurity.io/cis/oidc/token - UserInfo endpoint:
https://api.transmitsecurity.io/cis/oidc/me - Jwks_uri endpoint:
https://api.transmitsecurity.io/cis/oidc/jwks
- Issuer URL:
To synchronize user data between the two apps, navigate to the Attribute mapping section on the user pool page. There, specify the user attributes to map, which correspond to the identification method chosen for the integration. Each line corresponds to an attribute mapping.
- In the User pool attribute column, use the attribute as defined in AWS Cognito.
- In the OpenID Connect attribute column, use the attribute as defined in Mosaic as the external OpenID provider.
For example:
| User pool attribute | OpenID Connect attribute |
|---|---|
| phone_number | phone |
By determining the user attributes to map, you establish the way AWS Cognito interprets and uses the claims returned within the user tokens generated by Mosaic.
The configurations above guarantee a seamless integration of Mosaic passwordless authentication in your AWS Cognito app. As mentioned in the article, the integration's functionality depends on the mapping of user data between the apps. To ensure a stable mapping of user attributes, we recommend implementing an AWS Lambda function. This function activates upon the initial sign-in, completing the sign-up process, and verifies the mapping of user data.
In the example below, the function takes the user email data provided by Mosaic in association with the passkey, and checks if an existing account with the same email already exists in the User pool. If a match is found, it links the incoming user data with the existing Cognito data. Otherwise, a new user will also be created in the User pool.
const AWS = require('aws-sdk');
exports.handler = (event, context, callback) => {
//----------------Account Linking in case of sign-in with external IdP-----------------//
if(event.triggerSource === 'PreSignUp_ExternalProvider'){
var cognitoidentityserviceprovider =
new AWS.CognitoIdentityServiceProvider({region: event.region});
var sourceEmail = event.request.userAttributes.email;
var providerName = event.userName.split("_")[0];
var sourceAccountUserId = event.userName.split("_")[1];
console.log(sourceEmail, providerName,sourceAccountUserId);
//----------search for users with the same email
var filterStr = 'email = \"'+sourceEmail+'\"';
var searchParams = {
UserPoolId: event.userPoolId,
AttributesToGet: ['sub','email'],
Filter: filterStr
};
console.log("Searching for users",searchParams);
cognitoidentityserviceprovider.listUsers(searchParams, function(err, data) {
if (err){
console.log(err, err.stack); // an error occurred
callback(null, event); //continue sign-in flow
}else{
console.log("data.Users",data.Users);
if(data.Users != null && data.Users.length >=1){ //local account found
var destinationAccountUserName = data.Users[0]["Username"];
console.log("local account found",destinationAccountUserName);
var params = {
DestinationUser: {
ProviderAttributeName: 'cognito:username',
ProviderAttributeValue: destinationAccountUserName,
ProviderName: 'Cognito'
},
SourceUser: {
ProviderAttributeName: 'Cognito_Subject',
ProviderAttributeValue: sourceAccountUserId,
ProviderName: 'providerName'
},
UserPoolId: event.userPoolId
};
cognitoidentityserviceprovider.adminLinkProviderForUser(params,
function(err, data) {
if (err) {console.error("Error:"+err);callback(null, event);} // an error occurred
else{
//------accounts linking done, return error re_authentication_required
console.log("accounts linking done, return error re_authentication_required");
var error = new Error("re_authentication_required");
callback(error, event);
}
});
}else{
console.log("local account not found");
callback(null, event);
}
}
});
}else{ // not a sign-in with external IdP
// Return to Amazon Cognito
console.log("not a sign-in with external IdP");
callback(null, event);
}
};