Android SDK quick start
This guide describes how to quickly integrate Fraud Prevention into your Android application to get started. This includes both the client-side integration, as well as the backend API integration required to complete the flow.
Note
Client-side integrations are recommended for POCs and testing. For production environments, consider implementing Backend integration. Learn more about integration options: Client-side integration vs Backend integration.
How it works
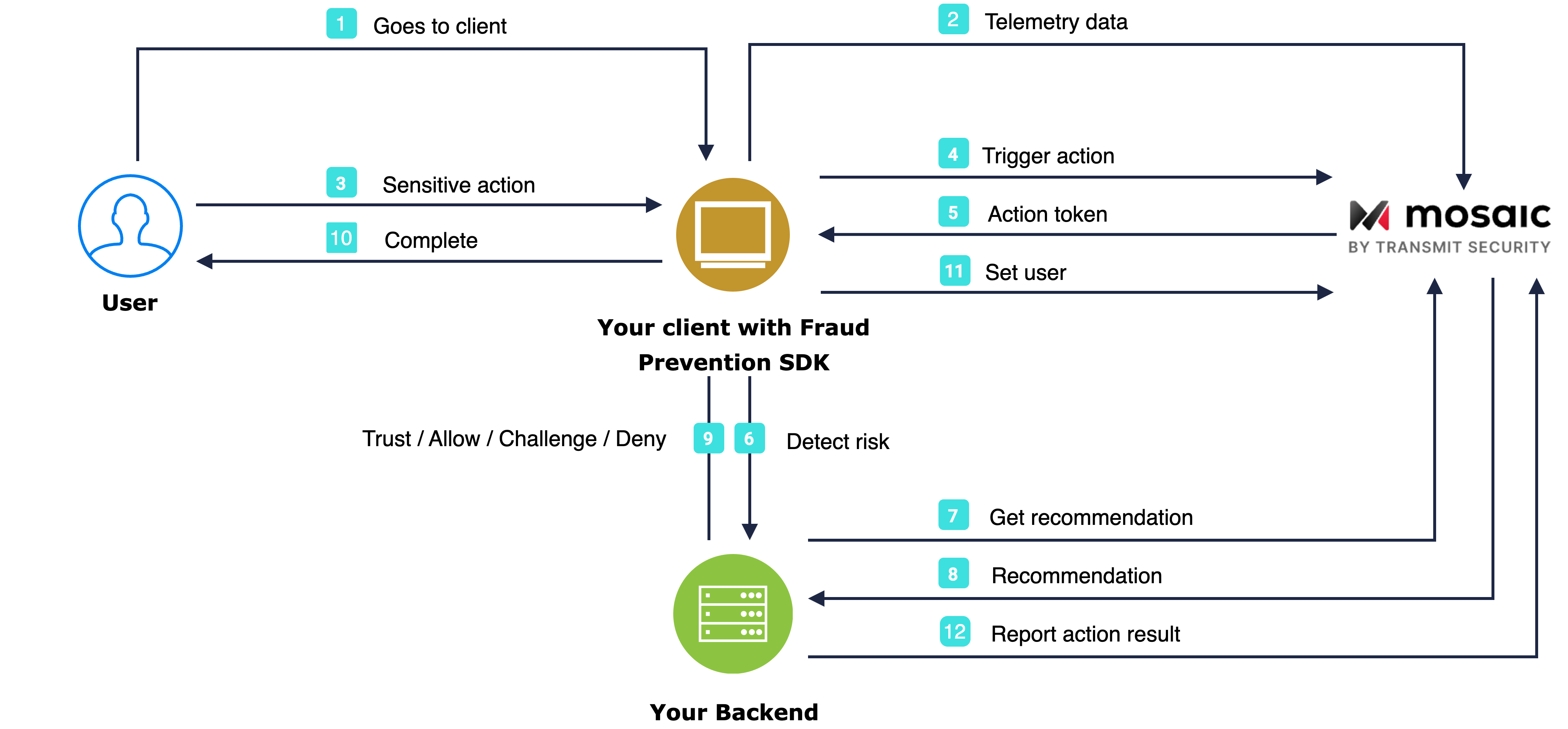
The flow starts with the user navigating to the Android app (1). The SDK gets initialized and starts sending telemetry to Mosaic (2). When a user performs an action, for example, clicks a login button (3), the SDK triggers an action event (4) and obtains an action token (5) which then forwards to the backend (6). Having received an action token, the application backend uses it to fetch recommendation from Mosaic (7 & 8) and instructs the client to act accordingly (9) in order to complete the login procedure (10). Upon successful login, the client sets the user (11). As a last optional step, your server can report the action result back to Mosaic (12).
Requirements
- Android 5+ (API level 21+)
Step 1: Get client credentials
Client credentials are used to identify your app and generate access tokens for authorizing Mosaic requests. To obtain them, you'll need to create an application in the Admin Portal (if you don’t have one yet).
- From Applications , click Add application .
- Add the friendly application name to display in the Admin Portal.
-
Add an OIDC client, specify the client secret as an authentication method, and your website URL as a redirect URI (e.g.,
https://your-domain.com).Note
These fields are required for all Mosaic apps, but won’t be used for Fraud Prevention.
- Click Add to create your application. This will automatically generate your client credentials.
Step 2: Add SDK to project
Add the following lines in the shared build.gradle file ("allprojects" scope):
dependencyResolutionManagement {
repositoriesMode.set(RepositoriesMode.FAIL_ON_PROJECT_REPOS)
repositories {
maven {
url('https://transmit.jfrog.io/artifactory/transmit-security-gradle-release-local/')
}
mavenCentral()
google()
}
}Add the following in the module build.gradle file (project scope):
dependencies {
implementation("com.ts.sdk:accountprotection:2.2.+")
}Step 3: Initialize SDK
Start monitoring your end-user risk levels by initializing and configuring the SDK.
Initialize using strings.xml configuration (recommended)
To do this, update the strings.xml file in your Application with the following content. The [CLIENT_ID] should be replaced with your client ID from step 1.
<resources>
<!-- Mosaic Credentials -->
<string name="transmit_security_client_id">"CLIENT_ID"</string>
<string name="transmit_security_base_url">https://api.transmitsecurity.io/</string>
</resources>Note
The SDK can be configured to work with different cluster by setting a third initialization parameter to baseUrl : 'https://api.transmitsecurity.io/risk-collect/' for US, or 'https://api.eu.transmitsecurity.io/' for EU or baseUrl : 'https://api.ca.transmitsecurity.io/' for Canada.
Add the code below to your Application class.
class Application : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
TSAccountProtection.initializeSDK(this)
}
}public class MyApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
TSAccountProtection.initializeSDK(this);
}
}Initialize using SDK parameters
Add the code below to your Application Class. The [CLIENT_ID] should be replaced with your client ID from step 1.
class Application : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
TSAccountProtection.initialize(this, "CLIENT_ID")
}
}public class MyApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
TSAccountProtection.initialize(this, "CLIENT_ID");
}
}Note
The SDK can be configured to work with different cluster by setting a third initialization parameter to baseUrl : 'https://api.transmitsecurity.io/risk-collect/' for US, or 'https://api.eu.transmitsecurity.io/' for EU or baseUrl : 'https://api.ca.transmitsecurity.io/' for Canada.
SDK session
Start an SDK session and obtain a session token after SDK initialization and prior to triggering events, and persist it on your backend. This step is optional for client-side integration but strongly recommended as it allows to transition to the backend integration—a session token is needed to trigger events from the backend and binds user's interactions to their device.
TSAccountProtection.getSessionToken(object : ISessionTokenCallback {
override fun onSessionToken(sessionToken: String) {
}
})Step 4: Trigger actions
To obtain risk recommendations for sensitive actions, your application should report these actions using the SDK. To do this, add the code below to relevant user interactions (e.g., the Login button click event handler). Replace [ACTION_TYPE] with the appropriate action type from our list of actions. ActionEventOptions and TransactionData objects are optional and could be set to null. To improve Fraud Prevention, optionally pass the correlation ID, and claimed user ID and its type (for users that haven't authenticated yet). This call returns actionToken, make sure to pass it to your backend to obtain the recommendation in the next step.
Note
For an alternative approach that directly utilizes our backend API instead, refer to our Backend API implementation guide.
// Optional, pass 'null' if not used
val payer = PayerData(
name = "PAYER_NAME",
bankIdentifier = "PAYER_BANK_IDENTIFIER",
branchIdentifier = "PAYER_BRANCH_IDENTIFIER",
accountNumber = "PAYER_ACCOUNT_NUMBER"
)
val payee = PayeeData(
name = "PAYEE_NAME",
bankIdentifier = "PAYEE_BANK_IDENTIFIER",
branchIdentifier = "PAYEE_BRANCH_IDENTIFIER",
accountNumber = "PAYEE_ACCOUNT_NUMBER"
)
TSAccountProtection.triggerAction(
"[ACTION_TYPE]",
// Optional, pass 'null' if not used
object : ActionEventOptions {
override val correlationId: String?
get() = correlationIdStr
override val claimUserId: String?
get() = claimUserIdStr
override val referenceUserId: String?
get() = referenceUserIdStr
},
// Optional, pass 'null' if not used
object : TransactionData {
override val amount: Double?
get() = amount
override val currency: String?
get() = currencyStr
override val payer: PayerData?
get() = payer
override val payee: PayeeData?
get() = payee
override val reason: String?
get() = reasonStr
override val transactionDate: Long?
get() = transactionDate
},
object : ITransmitSecurityTriggerActionEventCallback {
override fun onResponse(transmitSecurityTriggerActionResponse: TransmitSecurityTriggerActionResponse) {
val token = transmitSecurityTriggerActionResponse.token()
}
override fun onFailed(transmitSecurityAccountProtectionError: TransmitSecurityAccountProtectionError) {
val error = transmitSecurityAccountProtectionError.errorMessage
}
}
)//optional, pass 'null' if not used
PayerData payer = new PayerData("PAYER_NAME", "PAYER_BANK_IDENTIFIER", "PAYER_BRANCH_IDENTIFIER", "PAYER_ACCOUNT_NUMBER");
PayeeData payee = new PayeeData("PAYEE_NAME", "PAYEE_BANK_IDENTIFIER", "PAYEE_BRANCH_IDENTIFIER", "PAYEE_ACCOUNT_NUMBER");
TSAccountProtection.triggerAction("[ACTION_TYPE]",
//optional, pass 'null' if not used
new ActionEventOptions() {
@Nullable
@Override
public String getCorrelationId() {
return "CorrelationIdStr";
}
@Nullable
@Override
public String getClaimUserId() {
return "ClaimUserIdStr";
}
@Nullable
@Override
public String getReferenceUserId() {
return "ReferenceUserIdStr";
}
},
// Optional, pass 'null' if not used
new TransactionData() {
@Nullable
@Override
public Double getAmount() {
return amount;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public String getCurrency() {
return "currencyStr";
}
@Nullable
@Override
public PayerData getPayer() {
return payer;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public PayeeData getPayee() {
return payee;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public String getReason() {
return "reasonStr";
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Long getTransactionDate() {
return transactionDate;
}
},
new ITransmitSecurityTriggerActionEventCallback() {
@Override
public void onResponse(@NonNull TransmitSecurityTriggerActionResponse transmitSecurityTriggerActionResponse) {
String token = transmitSecurityTriggerActionResponse.token();
}
@Override
public void onFailed(@NonNull TransmitSecurityAccountProtectionError transmitSecurityAccountProtectionError) {
String error = transmitSecurityAccountProtectionError.getErrorMessage();
}
});Step 5: Fetch recommendation
You can fetch recommendations from your backend for the reported action using the Recommendation API. This is the same API that's also used for web integrations.
Mosaic APIs are authorized using an access token so you'll need to fetch a token using your client credentials (from step 1). The token should target the following resource: https://risk.identity.security. To do this, send the following request:
const { access_token } = await fetch(
`https://api.transmitsecurity.io/oidc/token`,
{
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
}
body: new URLSearchParams({
grant_type: client_credentials,
client_id: [CLIENT_ID],
client_secret: [CLIENT_SECRET],
resource: 'https://risk.identity.security'
})
}
);From your backend, invoke the Recommendation API by sending a request like the one below. The [ACCESS_TOKEN] is the authorization token you obtained using your client credentials and [ACTION_TOKEN] is the actionToken received from the SDK in Step 4.
const query = new URLSearchParams({
action_token: '[ACTION_TOKEN]',
}).toString();
const resp = await fetch(
`https://api.transmitsecurity.io/risk/v1/recommendation?${query}`,
{
method: 'GET',
headers: {
Authorization: 'Bearer [ACCESS_TOKEN]',
},
}
);Step 6: Set user
A user identifier must be reported to Mosaic after you've fully authenticated the user (including, for example, any required 2FA that was done). This will set the user for all subsequent events in the current device session, or until the app prompts the user to re-login, or until the user is explicitly cleared.
To do this, add the code below after your application has authenticated a user (or after SDK initialization if you already have the user context for the authenticated user). The [USER_ID] is an opaque identifier for the user in your system and must not include personal user identifiers, such as email, in plain text.
TSAccountProtection.setUserID(userId)TSAccountProtection.setUserID(userId);Note
For an alternative approach that directly utilizes our backend API instead, refer to our Backend API implementation guide.
Step 7: Clear user
The user gets automatically cleared once the device session expires or in case of a new login action. After the user logs out, you should clear the set user so they are not associated with future actions. To clear the user, call the clearUser() method:
TSAccountProtection.clearUser()TSAccountProtection.clearUser();